Each element P i j P_{ij} Pij is calculated as:
Step 4: Use the Markov Chain for Predictions
Use the transition probability matrix to predict future states. Given the current state, the future state probabilities can be calculated by multiplying the current state vector with the transition matrix.
If the current state vector is s0
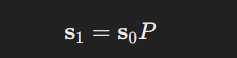
Step 5: Develop a Trading Strategy
Based on the predicted future states, develop a trading strategy. For example, if the model predicts a high probability of price increase (transitioning to an increasing state), you might decide to buy. Conversely, if a price decrease is predicted, you might decide to sell or short the asset.
Example in MQL5
Below is an example of how you might implement a simple Markov chain-based strategy in MQL5:
enum PriceState { DECREASE_SIGNIFICANTLY, DECREASE_SLIGHTLY, STABLE, INCREASE_SLIGHTLY, INCREASE_SIGNIFICANTLY }; PriceState GetState(double priceChange) { if (priceChange < -0.5) return DECREASE_SIGNIFICANTLY; if (priceChange < -0.1) return DECREASE_SLIGHTLY; if (priceChange < 0.1) return STABLE; if (priceChange < 0.5) return INCREASE_SLIGHTLY; return INCREASE_SIGNIFICANTLY; } double transitionMatrix[5][5] = { {0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, 0.1}, {0.1, 0.3, 0.4, 0.1, 0.1}, {0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1}, {0.1, 0.1, 0.3, 0.4, 0.1}, {0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.3} }; PriceState PredictNextState(PriceState currentState) { double rnd = MathRand() / (double)RAND_MAX; double cumulativeProbability = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cumulativeProbability += transitionMatrix[currentState][i]; if (rnd <= cumulativeProbability) { return (PriceState)i; } } return currentState; } void OnTick() { static PriceState currentState = STABLE; static double previousClose = 0.0; double currentClose = iClose(Symbol(), PERIOD_M1, 0); if (previousClose != 0.0) { double priceChange = (currentClose - previousClose) / previousClose * 100; currentState = GetState(priceChange); PriceState nextState = PredictNextState(currentState); if (nextState == INCREASE_SIGNIFICANTLY || nextState == INCREASE_SLIGHTLY) { if (PositionSelect(Symbol()) == false) { OrderSend(Symbol(), OP_BUY, 0.1, Ask, 2, 0, 0, "Buy Order", 0, 0, Green); } } else if (nextState == DECREASE_SIGNIFICANTLY || nextState == DECREASE_SLIGHTLY) { if (PositionSelect(Symbol()) == true) { OrderSend(Symbol(), OP_SELL, 0.1, Bid, 2, 0, 0, "Sell Order", 0, 0, Red); } } } previousClose = currentClose; }
Key Points:
- Define states: Based on price changes.
- Calculate transition probabilities: From historical data.
- Predict future states: Using the transition matrix.
- Develop strategy: Buy or sell based on predicted states.
Using Markov chains helps in capturing the probabilistic nature of price movements and can be a useful tool in developing trading strategies.